With the continuous development of the "
UAV +" era, the UAV industry can be applied to all walks of life, from consumer-grade aerial photography to industrial applications of drones. People can use the high-resolution CCD camera, thermal infrared camera, multi-lens camera and other sensor systems to obtain data to meet the needs of aerial photography, power line inspection, modeling and other industries.
In January 2017, Shanghai Bo Lei Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Bo Lei) successfully completed the long-term monitoring task of winter wheat in response to customer requirements.
Theoretical basis
There are many types of drones used in agriculture, such as
unmanned helicopters , fixed-wing drones, and multi-rotor drones. Bo Lei chose the multi-rotor UAV to assist in the operation. The advantages are as follows:
1) Relative to unmanned helicopters, multi-rotor operation is simple and low cost;
2) Compared with the fixed-wing UAV, the multi-rotor UAV can adjust the flight speed as needed, and the load is relatively large. Various sensors can be mounted as needed;
3) The multi-rotor UAV has controllable flight speed, adjustable flight height and low-altitude flight. At the same time, the multi-rotor UAV is not restricted by the take-off and landing site. The flight load is large and can be equipped with a variety of agricultural sensors.
The multi-spectral camera equipped with this agricultural monitoring has a total of five lenses, which correspond to near-infrared, red, green, red, and RGB. According to the collected data, the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) was selected to comprehensively reflect the growth distribution and coverage of winter wheat.
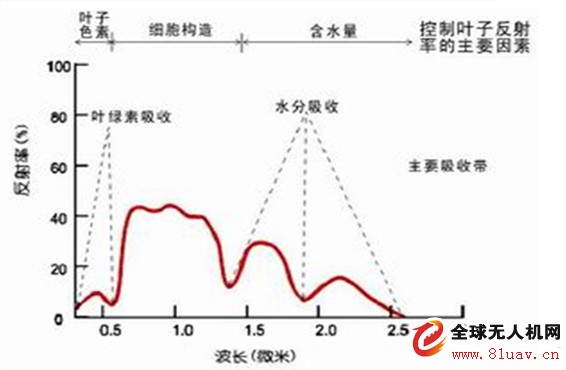
Plant foliage has strong absorption characteristics in the visible red light band and strong reflection characteristics in the near-infrared region, which is the physical basis for vegetation remote sensing monitoring. The NDVI index obtained by the combination of these two bands is sensitive to changes in soil background and can better identify vegetation and water bodies. When the vegetation is at medium and low coverage, the index increases rapidly with the increase of coverage. When it reaches a certain coverage, the growth is slow, so it is suitable for the dynamic monitoring of the early and middle growth stages of vegetation.
NDVI = (ρNIR-ρR)/(ρNIR+ρR)
Where: ρNIR is the reflectance in the near-infrared band, and ρR is the reflectance in the red band. The visible red light band (0.58-0.68 μm) is located in the chlorophyll absorption zone, and the near-infrared band (0.75-1.10 μm) is located in the high-reflection zone of the green plant spectrum.
NDVI range of values: -1 to 1, NDVI value of approximately 0 indicates bare soil area without vegetation; positive value of NDVI indicates vegetation coverage and increases with coverage, and greater than 0.7 indicates higher vegetation density in this area. The ground coverage cloud, water, snow area NDVI is negative. NDVI is the best indicator of plant spatial density and plant growth status, and is linearly related to the distribution density of vegetation cover. It is generally used to detect vegetation growth status and vegetation cover.
Practical application
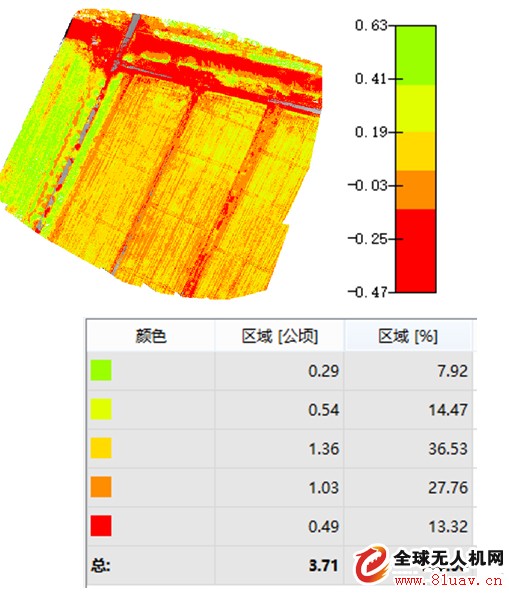
Ba Lei engineers photographed the monitoring area (57 acres) according to customer needs, 124 photos per lens, a total of 620. The shooting data is imported into the post-processing software Pix4D, and the RGB synthesized orthophoto image of the measurement area and the reflection map and the index map of each band can be obtained.
According to different needs, the bands can be combined to calculate the vegetation index, and the NDVI index map is calculated here. Combined with the chart, it can be seen that the red area indicates that there is a water area, the near-zero value is the road and the bare soil, the left green dense area has better vegetation coverage, and the right part is because the winter wheat is in the emergence stage, the leaf area is small, and the NDVI value is small. Showing a khaki color.
supplement
The chart shows the vegetation distribution and vegetation coverage ratio in this area during this period. In view of this situation, we can regularly monitor this area, and also use the NDVI index as the reference standard, so that the growth status of winter wheat growth period can be obtained, as the main basis for yield assessment and pest assessment, and monitoring wheat growth status from time to time. To improve the actual yield of wheat is significant.